M. Sc (Information Technology) PSIT1P4 Soft Computing Techniques
| Sr.No. | Name | ReadME |
|---|---|---|
| Prac1A-i Prac1A-ii |
1A-i. Design a simple linear neural network model. 1A-ii. Calculate the output of neural net for given data. |
Prac1A-i Prac1A-ii |
| Prac1B | 1B. Calculate the output of neural net using both binary and bipolar sigmoidal function. | Prac1B |
| Prac2A | 2A. Generate AND/NOT function using McCulloch- Pitts neural net. | Prac2A |
| Prac2B | 2B. Generate XOR function using McCulloch-Pitts neural net. | Prac2B |
| Prac3A | 3A. Write a program to implement Hebb’s rule. | Prac3A |
| Prac3B | 3B. Write a program to implement of delta rule. | Prac3B |
| Prac4A | 4A. Write a program for Back Propagation Algorithm. | Prac4A |
| Prac4B | 4B. Write a program for error Backpropagation algorithm. | Prac4B |
| Prac5A | 5A. Write a program for hopfield network. | Prac5A |
| Prac5B | 5B. Write a program for radial basis function. | Prac5B |
| Prac6A | 6A. Kohonen self organizing map. | Prac6A |
| Prac6B | 6B. Hopfield network. | Prac6B |
| Prac7A-i Prac7A-ii |
7A-i. Implement membership and identity operators - in 7A-ii. Implement membership and identity operators- not in. |
Prac7A-i Prac7A-ii |
| Prac7B-i Prac7B-ii |
7B-i. Implement membership and identity operators- is. 7B-ii. Implement membership and identity operators- is not. |
Prac7B-i Prac7B-ii |
| Prac8A | 8A. Find ratios using fuzzy logic. | Prac8A |
| Prac8B | 8B. Solve tipping problem using fuzzy logic. | Prac8B |
- 1A-i. Design a simple linear neural network model.
x = float(input("\n Enter the input x = "))
w = float(input("\n Enter the weight w = "))
b = float(input("\n Enter the bias b = "))
yin = w * x + b
print("\n Next input yin ", yin)
print("\n ************OUTPUT**************")
if yin < 0:
output = 0
elif yin > 1:
output = 1
else:
output = yin
print("Output", output)- OUTPUT
- 1A-ii. Calculate the output of neural net for given data.
# 1A-ii. Calculate the output of neural net for given data.
n = int(input("Enter the number of input: "))
yin = 0
for i in range(n):
x = float(input("Enter x :"))
w = float(input("Enter weight w: "))
yin = yin + x * w
print("Output ", yin)
if yin < 0:
output = 0
elif yin > 1:
output = 1
else:
output = yin
print("Output: ", output)- OUTPUT
- 1B. Calculate the output of neural net using both binary and bipolar sigmoidal function.
# 1B. Calculate the output of neural net using both binary and bipolar sigmoidal function.
import math
n = int(input("Enter the number of element "))
yin = 0
for i in range(0, n):
x = float(input("Enter x :"))
w = float(input("Enter weight w: "))
yin = yin + x * w
b = float(input("B "))
yin = yin + b
print("yin ", yin)
binary_sigmoidal = 1 / (1 + (math.e ** (-yin)))
print("Binary Sigmoidal = ", round(binary_sigmoidal, 3))
bipolar_sigmoidal = (2 / (1 + (math.e ** (-yin)))) - 1
print("Bipolar Sigmoidal = ", round(bipolar_sigmoidal, 3))- OUTPUT
- 2A. Generate AND/NOT function using McCulloch- Pitts neural net.
# 2A. Generate AND/NOT function using McCulloch- Pitts neural net.
print("ANDNOT function using McCulloch-pitts\n")
x1inputs = [1, 1, 0, 0]
x2inputs = [1, 0, 1, 0]
print("Considering one weight as excitatory and other as inhibitory")
w1 = [1, 1, 1, 1]
w2 = [-1, -1, -1, -1]
yin = []
print("x1", "x2", "yin")
for i in range(0, 4):
yin.append(x1inputs[i] * w1[i] + x2inputs[i] * w2[i])
print(x1inputs[i], " ", x2inputs[i], " ", yin[i])
theta = 2 * 1 - 1 # n *w -p
print("Threshold-theta - ", theta)
print("Applying Threshold - ", theta)
Y = []
for i in range(0, 4):
if yin[i] >= theta:
value = 1
Y.append(value)
else:
value = 0
Y.append(value)
print("x1 ", "x2", "Y")
for i in range(0, 4):
print(x1inputs[i], " ", x2inputs[i], " ", Y[i])- OUTPUT
- 2B. Generate XOR function using McCulloch-Pitts neural net.
# 2B. Generate XOR function using McCulloch-Pitts neural net.
print("XOR function using McCulloch-pitts\n")
x1inputs = [1, 1, 0, 0]
x2inputs = [1, 0, 1, 0]
print("Calculating z1 = x1w11 + x2w21")
print("Considering one weights as excitatory and other as inhibitory")
w11 = [1, 1, 1, 1]
w21 = [-1, -1, -1, -1]
print("x1", "x2", "z1")
z1 = []
for i in range(0, 4):
z1.append(x1inputs[i] * w11[i] + x2inputs[i] * w21[i])
print(x1inputs[i], " ", x2inputs[i], " ", z1[i])
# Z2
print("Calculating z2 = x1w12 + x2w22")
print("Considering one weights as inhibitory and other as excitatory")
w12 = [-1, -1, -1, -1]
w22 = [1, 1, 1, 1]
print("x1", "x2", "z2")
z2 = []
for i in range(0, 4):
z2.append(x1inputs[i] * w12[i] + x2inputs[i] * w22[i])
print(x1inputs[i], " ", x2inputs[i], " ", z2[i])
print("Applying threshold for x1 and x2")
for i in range(0, 4):
if z1[i] >= 1:
z1[i] = 1
else:
z1[i] = 0
if z2[i] >= 1:
z2[i] = 1
else:
z2[i] = 0
print("z1", "z2")
for i in range(0, 4):
print(z1[i], " ", z2[i])
print("x1 ", "x2", "Yin")
yin = []
v1 = 1
v2 = 1
for i in range(0, 4):
yin.append(z1[i] * v1 + z2[i] * v2)
print(x1inputs[i], " ", x2inputs[i], " ", yin[i])
print("Applying Threshold=1 for yin")
print("x1", "x2", "yin")
y = []
for i in range(0, 4):
if yin[i] >= 1:
y.append(1)
else:
y.append(0)
for i in range(0, 4):
print(x1inputs[i], " ", x2inputs[i], " ", y[i])
print("END")- OUTPUT
- 3A. Write a program to implement Hebb’s rule.
# 3A. Write a program to implement Hebb’s rule.
import numpy as np
x1 = np.array([1, -1, -1, 1, -1, -1, 1, 1, 1])
x2 = np.array([1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
b = 0
y = np.array([1, -1])
wtold = np.zeros((9,))
wtnew = np.zeros((9,))
wtnew = wtnew.astype(int)
wtold = wtold.astype(int)
bais = 0
print("First input with target = 1")
for i in range(0, 9):
wtnew[i] = wtold[i] + x1[i] * y[0]
wtold = wtnew
b = b + y[0]
print("New wt=", wtnew)
print("Bias value ", b)
print("**********************************")
print("second input with target = 1")
for i in range(0, 9):
wtnew[i] = wtold[i] + x2[i] * y[1]
wtold = wtnew
b = b + y[1]
print("New wt=", wtnew)
print("Bias value= ", b)- OUTPUT
- 3B. Write a program to implement of delta rule.
# 3B. Write a program to implement of delta rule.
print("b) Aim: - Write a program to implement delta rule")
import numpy as np
import time
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
x = np.zeros((3,))
weights = np.zeros((3,))
desired = np.zeros((3,))
actual = np.zeros((3,))
for i in range(0, 3):
x[i] = float(input("Intial inputs: "))
for i in range(0, 3):
weights[i] = float(input("Intial weights: "))
for i in range(0, 3):
desired[i] = float(input("Desired output: "))
a = float(input("Enter learning rate: "))
actual = x * weights
print("Acrual ", actual)
print("Desired ", desired)
while True:
if np.array_equal(desired, actual):
break
else:
for i in range(0, 3):
weights[i] = weights[i] + a * (desired[i] - actual[i])
actual = x * weights
print("Weights ", weights)
print("Actual ", actual)
print("Desired ", desired)
print("*" * 30)
print("Final output")
print("Corrected weights", weights)
print("Actual", actual)
print("Desired ", desired)- OUTPUT
- 4A. Write a program for Back Propagation Algorithm.
# 4A. Write a program for Back Propagation Algorithm.
import numpy as np
X = np.array(([2, 9], [1, 5], [3, 6]), dtype=float)
Y = np.array(([92], [86], [89]), dtype=float)
X = X / np.amax(X, axis=0)
Y = Y / 100
class NN(object):
def __init__(self):
self.inputsize = 2
self.outputsize = 1
self.hiddensize = 3
self.W1 = np.random.randn(self.inputsize, self.hiddensize)
self.W2 = np.random.randn(self.hiddensize, self.outputsize)
def forward(self, X):
self.z = np.dot(X, self.W1)
self.z2 = self.sigmoidal(self.z)
self.z3 = np.dot(self.z2, self.W2)
op = self.sigmoidal(self.z3)
return op
def sigmoidal(self, s):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-s))
obj = NN()
op = obj.forward(X)
print("actual output\n" + str(op))
print("expected output\n" + str(Y))- OUTPUT
- 4B. Write a program for error Backpropagation algorithm.
# 4B. Write a program for error Backpropagation algorithm.
import numpy as np
X = np.array(([2, 9], [1, 5], [3, 6]), dtype=float)
Y = np.array(([92], [86], [89]), dtype=float)
X = X / np.amax(X, axis=0)
Y = Y / 100
class NN(object):
def __init__(self):
self.inputsize = 2
self.outputsize = 1
self.hiddensize = 3
self.W1 = np.random.randn(self.inputsize, self.hiddensize)
self.W2 = np.random.randn(self.hiddensize, self.outputsize)
def forward(self, X):
self.z = np.dot(X, self.W1)
self.z2 = self.sigmoidal(self.z)
self.z3 = np.dot(self.z2, self.W2)
op = self.sigmoidal(self.z3)
return op
def sigmoidal(self, s):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-s))
def sigmoidalprime(self, s):
return s * (1 - s)
def backward(self, X, Y, o):
self.o_error = Y - o
self.o_delta = self.o_error * self.sigmoidalprime(o)
self.z2_error = self.o_delta.dot(self.W2.T)
self.z2_delta = self.z2_error * self.sigmoidalprime(self.z2)
self.W1 = self.W1 + X.T.dot(self.z2_delta)
self.W2 = self.W2 + self.z2.T.dot(self.o_delta)
def train(self, X, Y):
o = self.forward(X)
self.backward(X, Y, o)
obj = NN()
for i in range(2000):
print("input\n" + str(X))
print("Actual output\n" + str(Y))
print("Predicted output\n" + str(obj.forward(X)))
print("loss\n" + str(np.mean(np.square(Y - obj.forward(X)))))
obj.train(X, Y)- OUTPUT
- 5A. Write a program for hopfield network.
# 5A. Write a program for hopfield network.
import numpy as np
def compute_next_state(state, weight):
# @ is a shorthand for 'np.matmul()'
# the numpy.where() function return thr indices of
# element in an input array where condition is satisfied
next_state = np.where(weight @ state >= 0, +1, -1)
return next_state
def compute_final_state(initial_state, weight, max_iter=1000):
previous_state = initial_state
next_state = compute_next_state(previous_state, weight)
is_stable = np.all(previous_state == next_state)
n_iter = 0
while (not is_stable) and (n_iter <= max_iter):
previous_state = next_state
next_state = compute_next_state(previous_state, weight)
print("Previous State: ", previous_state)
print("Next State: ", next_state)
is_stable = np.all(previous_state == next_state)
n_iter += 1
return previous_state, is_stable, n_iter
initial_state = np.array([+1, -1, -1, -1])
weight = np.array([[0, -1, -1, +1], [-1, 0, +1, -1], [-1, +1, 0, -1], [+1, -1, -1, 0]])
final_state, is_stable, n_iter = compute_final_state(initial_state, weight)
print("final State : ", final_state)
print("is_stable : ", is_stable)- OUTPUT
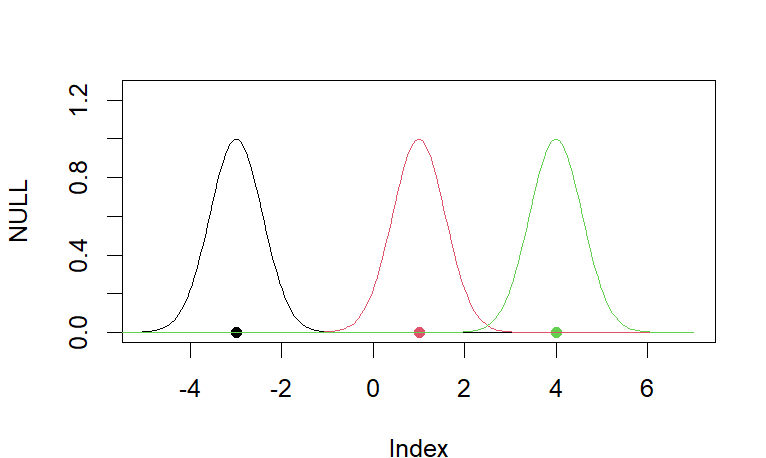
- 5B. Write a program for radial basis function(R language).
# 5B. Write a program for radial basis function.
# R language
D <- matrix(c(-3, 1, 4), ncol = 1) # 3 datapoints
N <- length(D)
rbf.gauss <- function(gamma = 1.0) {
function(x) {
exp(-gamma * norm(as.matrix(x), "F")^2)
}
}
xlim <- c(-5, 7)
print(N)
print(xlim)
plot(NULL, xlim = xlim, ylim = c(0, 1.25), type = "n")
points(D, rep(0, length(D)), col = 1:N, pch = 19)
x.coord <- seq(-7, 7, length = 250)
gamma <- 1.5
for (i in 1:N) {
points(x.coord, lapply(x.coord - D[i, ], rbf.gauss(gamma)), type = "l", col = i)
}- OUTPUT
- 6A. Kohonen self organizing map
# 6A. Kohonen self organizing map.
from minisom import MiniSom
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
colors = [
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 0.5],
[0.125, 0.529, 1.0],
[0.33, 0.4, 0.67],
[0.6, 0.5, 1.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 1.0],
[1.0, 0.0, 1.0],
[1.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
[0.33, 0.33, 0.33],
[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
[0.66, 0.66, 0.66],
]
color_names = [
"black",
"blue",
"darkblue",
"skyblue",
"greyblue",
"lilac",
"green",
"red",
"cyan",
"violet",
"yellow",
"white",
"darkgrey",
"mediumgrey",
"lightgrey",
]
som = MiniSom(30, 30, 3, sigma=3.0, learning_rate=2.5, neighborhood_function="gaussian")
plt.imshow(abs(som.get_weights()), interpolation="none")
som = MiniSom(30, 30, 3, sigma=8.0, learning_rate=0.5, neighborhood_function="bubble")
som.train_random(colors, 500, verbose=True)
plt.imshow(abs(som.get_weights()), interpolation="none")- OUTPUT
- 6B. Hopfield network.
# 6B. Hopfield network.
from neurodynex.hopfield_network import network, pattern_tools, plot_tools
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
pattern_size = 5
# create an instance of the class HopfieldNetwork
hopfield_net = network.HopfieldNetwork(nr_neurons=pattern_size ** 2)
# instantiate a pattern factory
factory = pattern_tools.PatternFactory(pattern_size, pattern_size)
# create a checkerboard pattern and add it to the pattern list
checkerboard = factory.create_checkerboard()
pattern_list = [checkerboard]
# add random patterns to the list
pattern_list.extend(
factory.create_random_pattern_list(nr_patterns=3, on_probability=0.5)
)
plot_tools.plot_pattern_list(pattern_list)
# how similar are the random patterns and the checkerboard? Check the overlaps
overlap_matrix = pattern_tools.compute_overlap_matrix(pattern_list)
plot_tools.plot_overlap_matrix(overlap_matrix)
# let the hopfield network "learn" the patterns. Note: they are not stored
# explicitly but only network weights are updated !
hopfield_net.store_patterns(pattern_list)
# create a noisy version of a pattern and use that to initialize the network
noisy_init_state = pattern_tools.flip_n(checkerboard, nr_of_flips=4)
hopfield_net.set_state_from_pattern(noisy_init_state)
# from this initial state, let the network dynamics evolve.
states = hopfield_net.run_with_monitoring(nr_steps=4)
# each network state is a vector. reshape it to the same shape used to create the patterns.
states_as_patterns = factory.reshape_patterns(states)
# plot the states of the network
plot_tools.plot_state_sequence_and_overlap(
states_as_patterns, pattern_list, reference_idx=0, suptitle="Network dynamics"
)- OUTPUT
- 7A-i. Implement membership and identity operators in
# 7A-i. Implement membership and identity operators *in*.
list1 = []
print("Enter 5 numbers")
for i in range(0, 5):
v = int(input())
list1.append(v)
list2 = []
print("Enter 5 numbers")
for i in range(0, 5):
v = int(input())
list2.append(v)
flag = 0
for i in list1:
if i in list2:
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
print("The Lists Overlap")
else:
print("The Lists do Not overlap")- OUTPUT
- 7A-ii. Implement membership and identity operators not in
# 7A-ii. Implement membership and identity operators *not in*.
list1 = []
c = int(input("Enter the number of elements that you want to insert in List 1:"))
for i in range(0, c):
ele = int(input("Enter the element :"))
list1.append(ele)
a = int(input("enter the number that you want to find in List 1:"))
if a not in list1:
print("The list does not contain ", a)
else:
print("The list contains", a)- OUTPUT
- 7B-i. Implement membership and identity operators is.
# 7B-i. Implement membership and identity operators *is*.
details = []
name = input("Enter your name : ")
details.append(name)
age = float(input("Enter your exact age : "))
details.append(age)
roll_no = int(input("Enter your roll no : "))
details.append(roll_no)
for i in details:
print(i)
print("Int = ", type(i) is int)
print("Float = ", type(i) is float)
print("String = ", type(i) is str)
print()- OUTPUT
- 7B-ii. Implement membership and identity operators is not.
# 7B-ii. Implement membership and identity operators *is not*.
details = []
name = input("Enter your name : ")
details.append(name)
age = float(input("Enter your exact age : "))
details.append(age)
roll_no = int(input("Enter your roll no : "))
details.append(roll_no)
print()
for i in details:
print(i)
print("Not Int = ", type(i) is not int)
print("Not Float = ", type(i) is not float)
print("Not String = ", type(i) is not str)
print()- OUTPUT
- 8A. Find ratios using fuzzy logic.
# 8A. Find ratios using fuzzy logic.
from fuzzywuzzy import fuzz
from fuzzywuzzy import process
s1 = "My name is ABC"
s2 = "I am ABC"
print("FuzzyWuzzy Ratio:", fuzz.ratio(s1, s2))
print("FuzzyWuzzy PartialRatio: ", fuzz.partial_ratio(s1, s2))
print("FuzzyWuzzy TokenSortRatio: ", fuzz.token_sort_ratio(s1, s2))
print("FuzzyWuzzy TokenSetRatio: ", fuzz.token_set_ratio(s1, s2))
print("FuzzyWuzzy WRatio: ", fuzz.WRatio(s1, s2), "\n\n")
# for process library,
query = "fuzzys for fuzzys"
choices = ["fuzzy for fuzzy", "fuzzy fuzzy", "g. for fuzzys"]
print("List of ratios: ")
print(process.extract(query, choices), "\n")
print("Best among the above list: ", process.extractOne(query, choices))- OUTPUT
- 8B. Solve tipping problem using fuzzy logic.
# 8B. Solve tipping problem using fuzzy logic.
# google.colab
!pip install fuzzywuzzy
!pip install -U scikit-fuzzy
import skfuzzy as fuzz
from skfuzzy import control as ctrl
import numpy as np
quality = ctrl.Antecedent(np.arange(0, 11, 1), 'quality')
service = ctrl.Antecedent(np.arange(0, 11, 1), 'service')
tip = ctrl.Consequent(np.arange(0, 26, 1), 'tip')
quality.automf(3)
service.automf(3)
tip['low'] = fuzz.trimf(tip.universe, [0, 0, 13])
tip['medium'] = fuzz.trimf(tip.universe, [0, 13, 25])
tip['high'] = fuzz.trimf(tip.universe, [13, 25, 25])
quality['average'].view()
service.view()
tip.view()
rule1 = ctrl.Rule(quality['poor'] | service['poor'], tip['low'])
rule2 = ctrl.Rule(service['average'], tip['medium'])
rule3 = ctrl.Rule(service['good'] | quality['good'], tip['high'])
rule1.view()
tipping_ctrl = ctrl.ControlSystem([rule1, rule2, rule3])
tipping = ctrl.ControlSystemSimulation(tipping_ctrl)
tipping.input['quality'] = 6.5
tipping.input['service'] = 9.8
tipping.compute()
print (tipping.output['tip'])
tip.view(sim=tipping)- OUTPUT