| title | abbrlink | tags |
|---|---|---|
2019-02-01-algorithms4-2 |
afac |
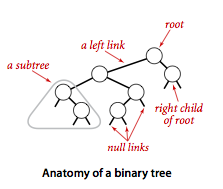
二叉树 是一个空链接,或者是一个有左右两个链接的节点,每个链接都指向一颗子二叉树。
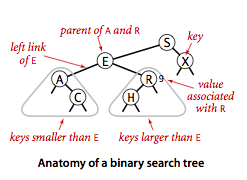
二叉查找树 (BST)是一颗二叉树,并且每个节点的值都大于等于其左子树中的所有节点的值而小于等于右子树的所有节点的值。
BST 有一个重要性质,就是它的中序遍历结果递增排序。
public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> implements OrderedST<Key, Value> {
protected Node root;
protected class Node {
Key key;
Value val;
Node left;
Node right;
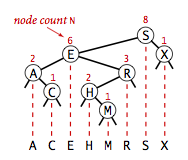
// 以该节点为根的子树节点总数
int N;
// 红黑树中使用
boolean color;
Node(Key key, Value val, int N) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.N = N;
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
return size(root);
}
private int size(Node x) {
if (x == null)
return 0;
return x.N;
}
protected void recalculateSize(Node x) {
x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
}
}主要有查找、删除、插入三个操作。
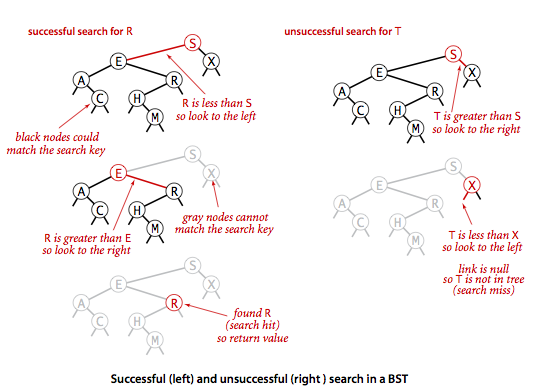
- 如果树是空的,则查找未命中;
- 如果被查找的键和根节点的键相等,查找命中;
- 否则递归地在子树中查找:如果被查找的键较小就在左子树中查找,较大就在右子树中查找。
public Value get(Key key) {
return get(root, key);
}
private Value get(Node x, Key key) {
// 在以 x 为根结点的子树中查找并返回 key 所对应的值
if(x == null)
return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if(cmp < 0)
return get(x.left, key);
else if(cmp > 0)
return get(x.right, key);
else
return x.val;
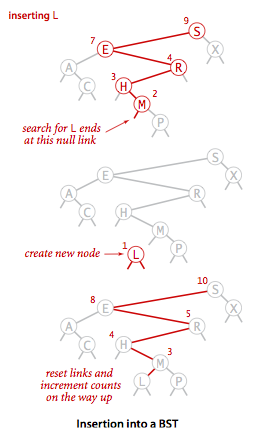
}当插入的键不存在于树中,需要创建一个新节点,并且更新上层节点的链接指向该节点,使得该节点正确地链接到树中。
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
// 查找 key,找到则更新它的值,否则为它创建一个新的结点
root = put(root, key, val);
}
private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value val) {
// 如果 key 存在于以 x 为根结点的子树中则更新它的值;
// 否则将以 key 和 val 为键值对的新结点插入到该子树中
if(x == null)
return new Node(key, val, 1);
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if(cmp < 0)
x.left = put(x.left, key, val);
else if(cmp > 0)
x.right = put(x.right, key, val);
else
x.val = val;
x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
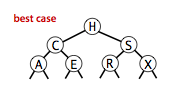
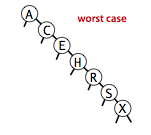
}二叉查找树的算法运行时间取决于树的形状,而树的形状又取决于键被插入的先后顺序。
最好的情况下树是完全平衡的,每条空链接和根节点的距离都为 logN。
在最坏的情况下,树的高度为 N。
利用二叉平衡树的有序性可以很快的用递归算法找到 min 与 max。
public Key max() {
return max(root).key;
}
private Node max(Node x) {
if(x.right == null)
return x;
return min(x.right);
}
public Key min() {
return min(root).key;
}
private Node min(Node x) {
if(x.left == null)
return x;
return min(x.left);
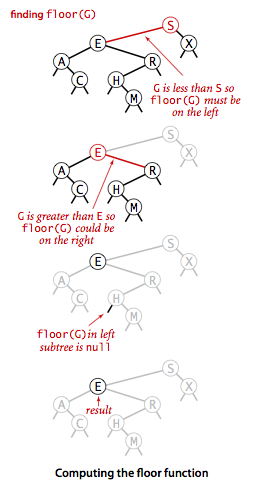
}public Key floor(Key key) {
Node x = floor(root, key);
if(x == null)
return null;
return x.key;
}
private Node floor(Node x, Key key) {
if(x == null)
return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if(cmp == 0)
return x;
if(cmp < 0)
return floor(x.left, key);
Node t = floor(x.right, key);
if(t != null)
return t;
else
return x;
}rank(key) 返回 key 的排名。
- 如果键和根节点的键相等,返回左子树的节点数;
- 如果小于,递归计算在左子树中的排名;
- 如果大于,递归计算在右子树中的排名,加上左子树的节点数,再加上 1(根节点)。
@Override
public int rank(Key key) {
return rank(key, root);
}
private int rank(Key key, Node x) {
if (x == null)
return 0;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp == 0)
return size(x.left);
else if (cmp < 0)
return rank(key, x.left);
else
return 1 + size(x.left) + rank(key, x.right);
}二叉查找树最难实现的就是 delete() 操作。
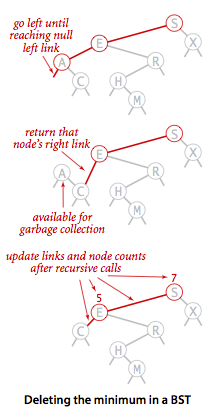
现看如何删除最小键 deletemin():
public void deleteMin() {
root = deleteMin(root);
}
private Node deleteMin(Node x) {
if(x.left == null)
return x.right;
x.left = deleteMin(x.left);
x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
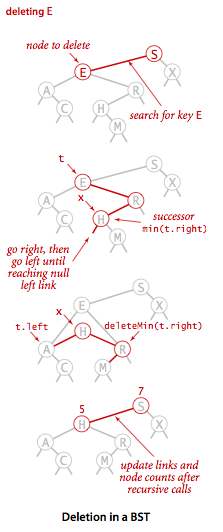
}再看删除一般节点的情况,对于删除一个拥有两个子结点的情况,在删除结点 x 后用它的后继结点填补它的位置。因为 x 有一个右子结点,因此它的后继结点就是其右子树中的最小结点。这样的替换仍然能保证树的有序性,因为 x.key 和它的后继结点的键之间不存在其他的键。
用 4 个简单的步骤能够完成将 x 替换为它的后继结点的任务:
- 将指向即将被删除的结点的链接保存为 t;
- 将 x 指向它的后继结点
min(t.right); - 将 x 的右链接(原本指向一棵所有结点都大于 x.key 的二叉查找树)指向
deleteMin(t.right),也就是在删除后所有结点仍然大于 x.key 的子二叉查找树; - 将 x 的左链接(本为空)设为 t.left(其下所有的键都小于被删除的结点和它的后继结点)。
对于某些大规模的实际应用,这种方法可能会有一点性能上的问题。
public void delete(Key key) {
root = delete(root, key);
}
private Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
if(x == null)
return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if(cmp < 0)
x.left = delete(x.left, key);
else if(cmp > 0)
x.right = delete(x.right, key);
else {
if(x.right == null)
return x.left;
if(x.left == null)
return x.right;
Node t = x;
x = min(t.right);
x.right = deleteMin(t.right);
x.left = t.left;
}
x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}利用二叉查找树中序遍历的结果为递增的特点。
public Iterable<Key> keys() {
return keys(min(), max());
}
public Iterable<Key> keys(Key lo, Key hi) {
Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>();
keys(root, queue, lo, hi);
return queue;
}
private void keys(Node x, Queue<Key> queue, Key lo, Key hi) {
if(x == null)
return;
int cmplo = lo.compareTo(x.key);
int cmphi = hi.compareTo(x.key);
if(cmplo < 0)
keys(x.left, queue, lo, hi);
if(cmplo <= 0 && cmplo >= 0)
queue.enqueue(x.key);
if(cmphi > 0)
keys(x.right, queue, lo, hi);
}二叉查找树所有操作在最坏的情况下所需要的时间都和树的高度成正比。